Tag: Models
Search News
Categories
Archives
Building a human tumour microenvironment in the lab
15th June 2021
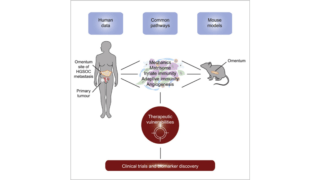
Researchers from Barts Cancer Institute at Queen Mary University of London, led by Professor Fran Balkwill and Dr Oliver Pearce, have built two 3D multi-cellular models of the human tumour microenvironment (TME) in ovarian cancer. The models, which are the first created from the CanBuild project, have revealed novel insights into the role of the TME in cancer progression.
Read moreImpact of chemotherapy on immune cells in the TME
10th April 2021
Research from Barts Cancer Institute, Queen Mary University of London, has revealed novel insights into the effects of chemotherapy on the tumour microenvironment (TME). The study found that chemotherapy enhances the anti-tumour actions of immune cells within the TME and their ability to support immune responses against cancer.
Read moreLondon Pancreas Workshop 2020
30th September 2020
On 11th September 2020, Professors Hemant Kocher and Nick Lemoine hosted the eighth London Pancreas Workshop (LPW) – a forum for state-of-the-art clinical and basic research in pancreatic cancer. In a first for the biennial event, this year’s LPW took place online with pre-recorded speaker presentations and live, interactive Q&A sessions.
Read moreMouse models of ovarian cancer
27th January 2020
Research led by the Barts Cancer Institute, Queen Mary University of London, has revealed that mouse models of the most common and deadly form of ovarian cancer, high-grade serous ovarian cancer, can effectively replicate the disease in humans. These models provide useful pre-clinical tools that may help to determine which patients are likely to respond to particular treatments.
Read moreFirst steps towards a vaccine for pancreatic cancer
26th November 2019
Researchers from Barts Cancer Institute and Zhengzhou University have developed a personalised vaccine system that could ultimately delay the onset of pancreatic cancer. The study reports the team’s work with a pre-clinical model using mice, and provides strong proof-of-concept for the creation of a vaccine for cancer prevention in individuals at high risk of developing this disease.
Read moreAntibody therapy in pancreatic cancer
31st July 2019
Scientists have found a way to target and knock out a single protein that they have discovered is widely involved in pancreatic cancer cell growth, survival and invasion. Called avb6, the protein is present on the surface of more than 80 per cent of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma – the most common form of pancreatic cancer – and is vital to increase the successful growth and spread of the tumour cells.
Read more